- 0317-4123373
- Bahria University Road D2 Johar Town Lahore, Pakistan
- Working Hour: Monday To Tuesday 04PM – 06PM
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a significant medical disorder that can be treated. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is the first step toward effective management and prevention. This guide provides clear, expert information to help you navigate your health journey with confidence.
Deep Vein Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot, or thrombus, forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in the legs. While DVT can affect anyone, knowing the signs is crucial for early detection and preventing serious complications, such as a pulmonary embolism, where a clot travels to the lungs.
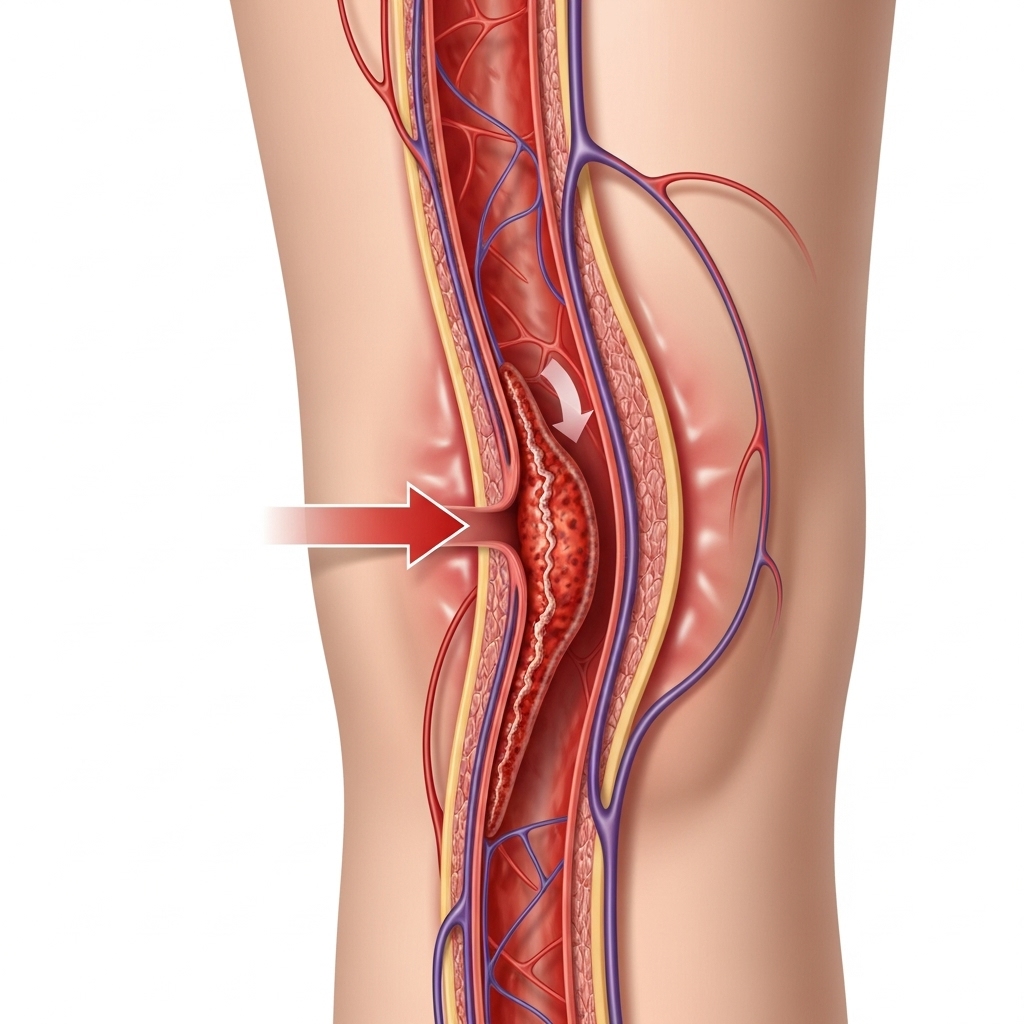
Symptoms often appear in one leg and can include:
Some people may not experience any symptoms at all, making it important to understand the risk factors.
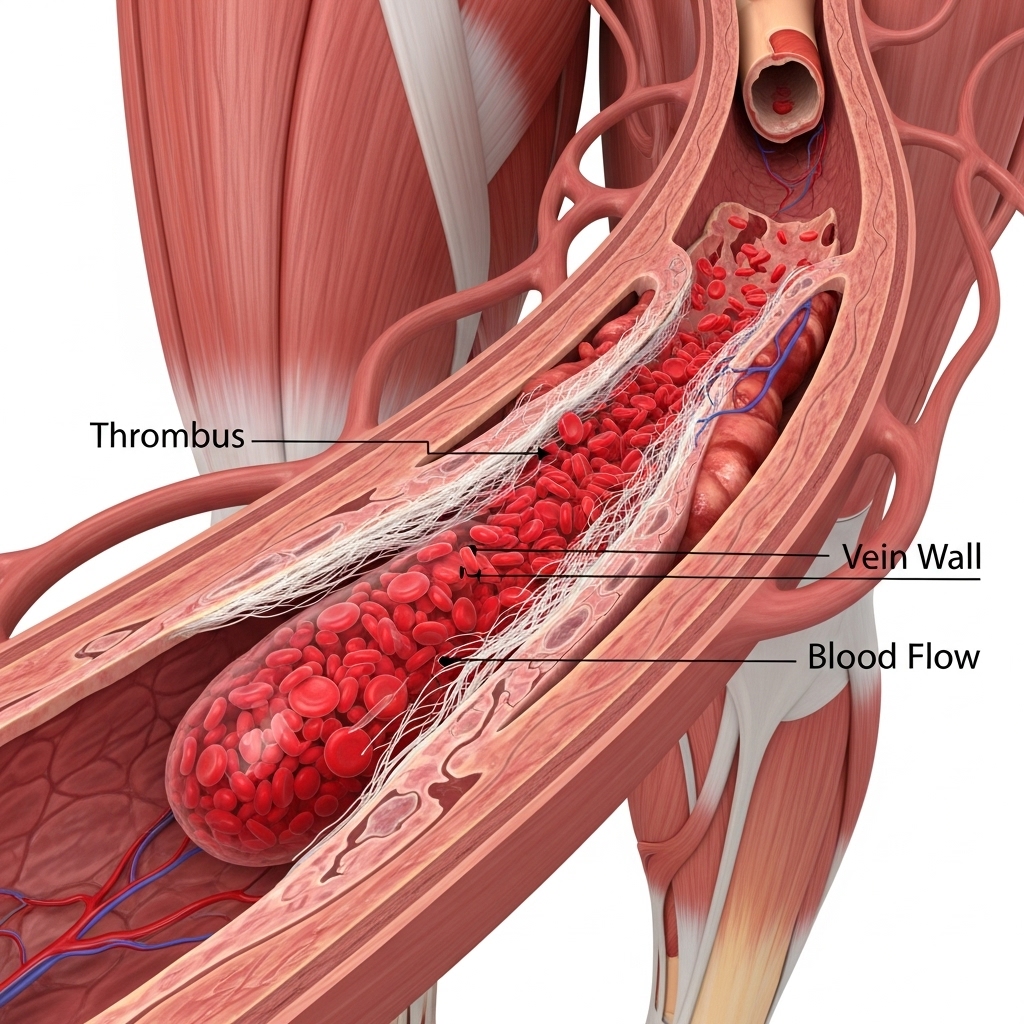
DVT is caused by anything that prevents your blood from circulating or clotting normally. The primary causes include:
Accurate diagnosis is key to effective DVT treatment. A vascular specialist may use several methods:

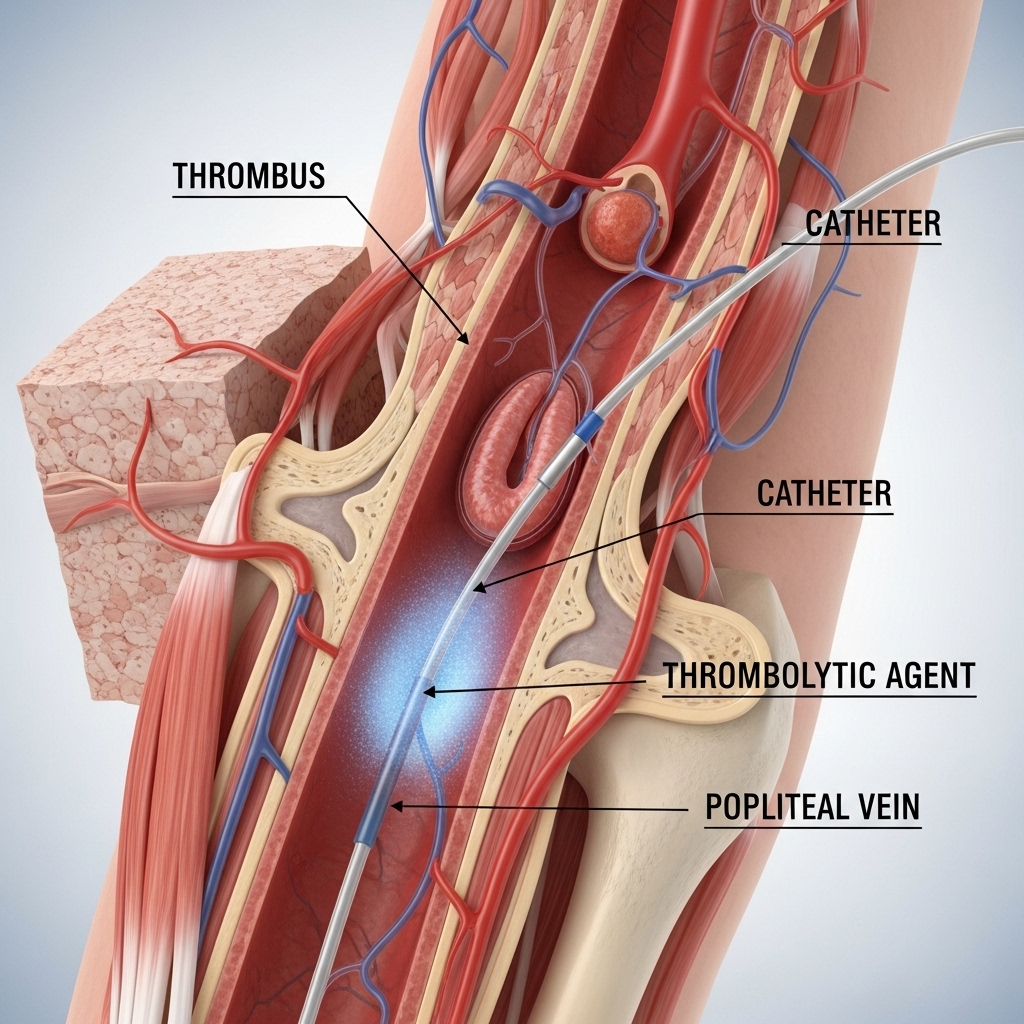
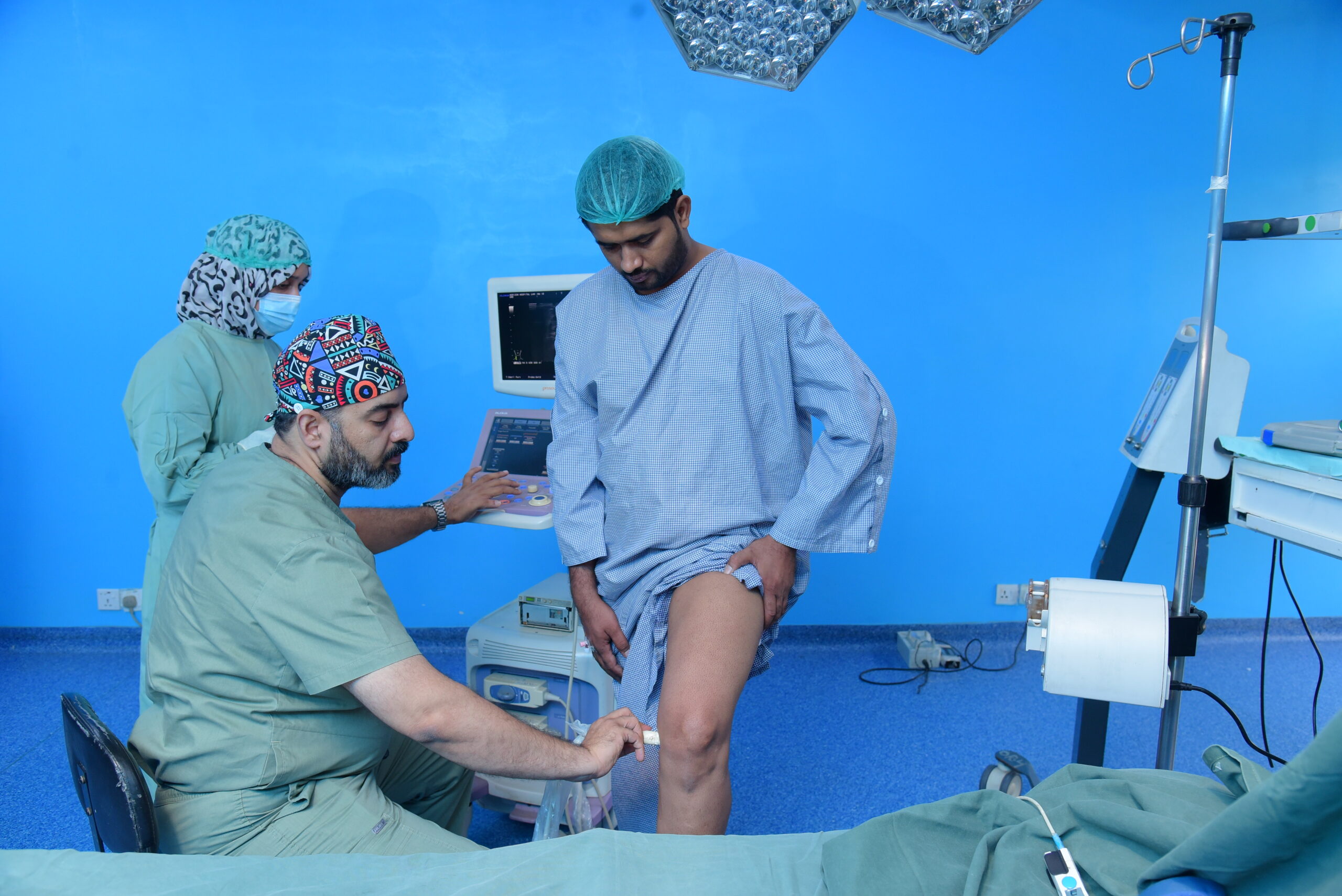
Patients with DVT typically present with the symptoms listed above, most commonly unilateral leg swelling and pain. A thorough physical examination by a qualified doctor is essential to assess the likelihood of DVT and determine the next steps for diagnosis.
The most serious complication of DVT is a Pulmonary Embolism (PE), which can be life-threatening. Another long-term issue is Post-Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS), which can cause chronic leg pain, swelling, and skin changes.
You can take steps to reduce your risk, especially if you know you’ll be immobile for a long time:
With timely and appropriate treatment, blood clots can dissolve, and the risk of complications can be significantly reduced. However, some individuals may have a long-term risk of recurrence and require ongoing management.
Recovery time varies depending on the size of the clot and the individual's overall health. It may take weeks or even months for the symptoms to get better. Following your doctor's treatment plan is essential for a successful recovery.
Yes, but it is important to take precautions. Consult your doctor before long trips, wear compression stockings, stay hydrated, and move your legs frequently during travel.
The best treatment is personalized to the patient. It typically involves blood-thinning medications and management by a qualified vascular surgeon who can provide a comprehensive care plan.