- 0317-4123373
- Bahria University Road D2 Johar Town Lahore, Pakistan
- Working Hour: Monday To Tuesday 04PM – 06PM
If left untreated, carotid artery disease is a severe condition that can result in a stroke. Understanding your risk and seeking timely medical care is the first step toward protecting your long-term health. With advanced diagnostic tools and personalized treatment, you can effectively manage this condition and reduce the likelihood of severe complications.

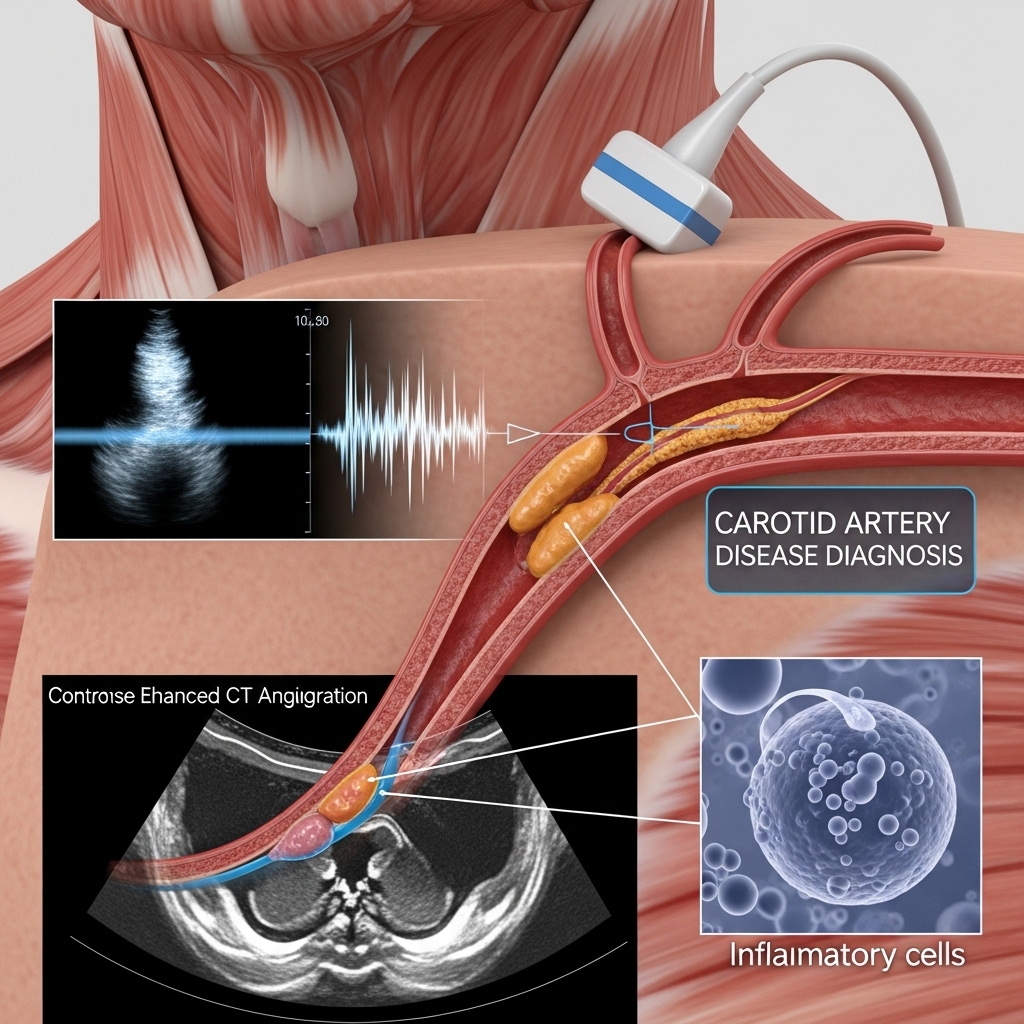
In its early stages, carotid artery disease often presents no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, you may experience a transient ischemic attack (TIA), often called a “mini stroke.” TIAs are temporary blockages and serve as critical warning signs. Symptoms appear suddenly and can include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Dr. Usman Jamil Mughal utilizes state-of-the-art diagnostic methods to assess the severity of the blockage and create a tailored management plan.
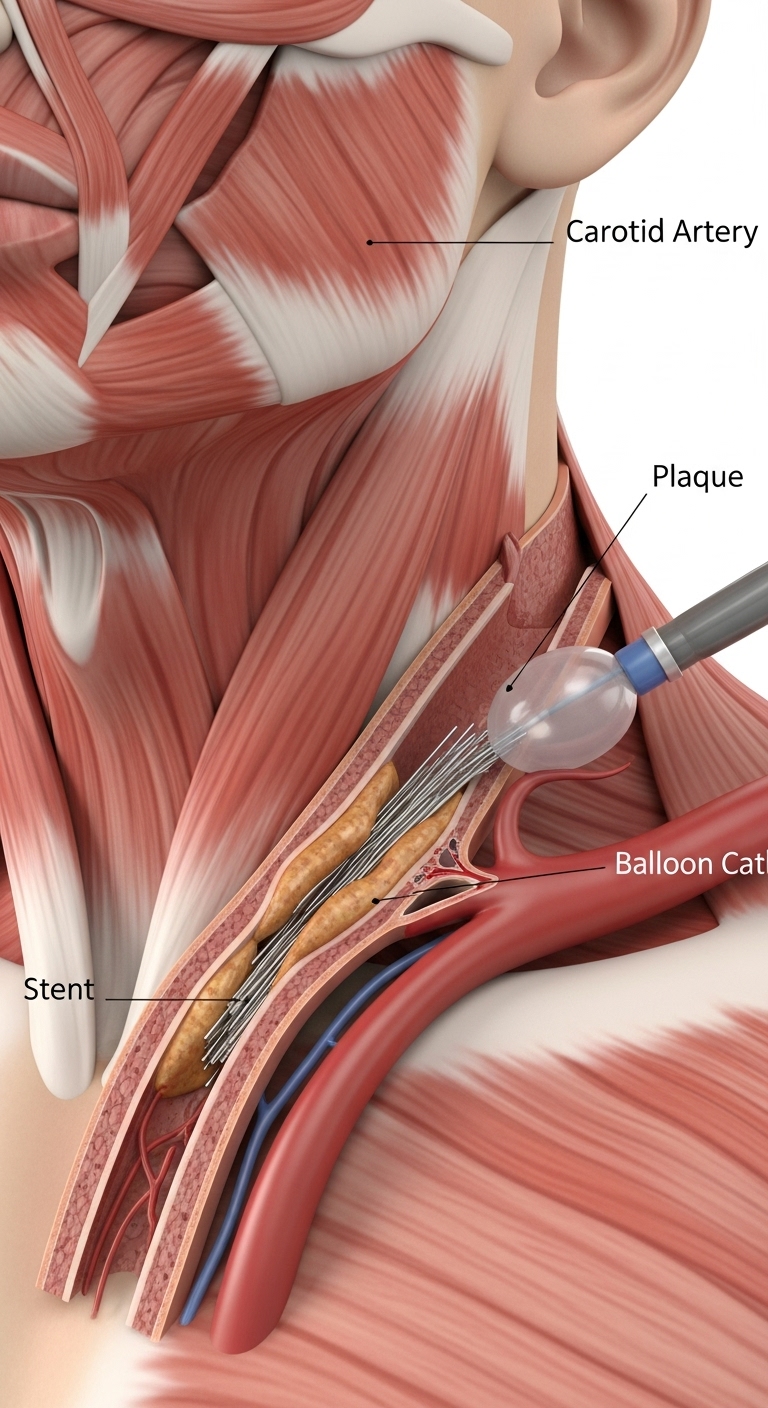
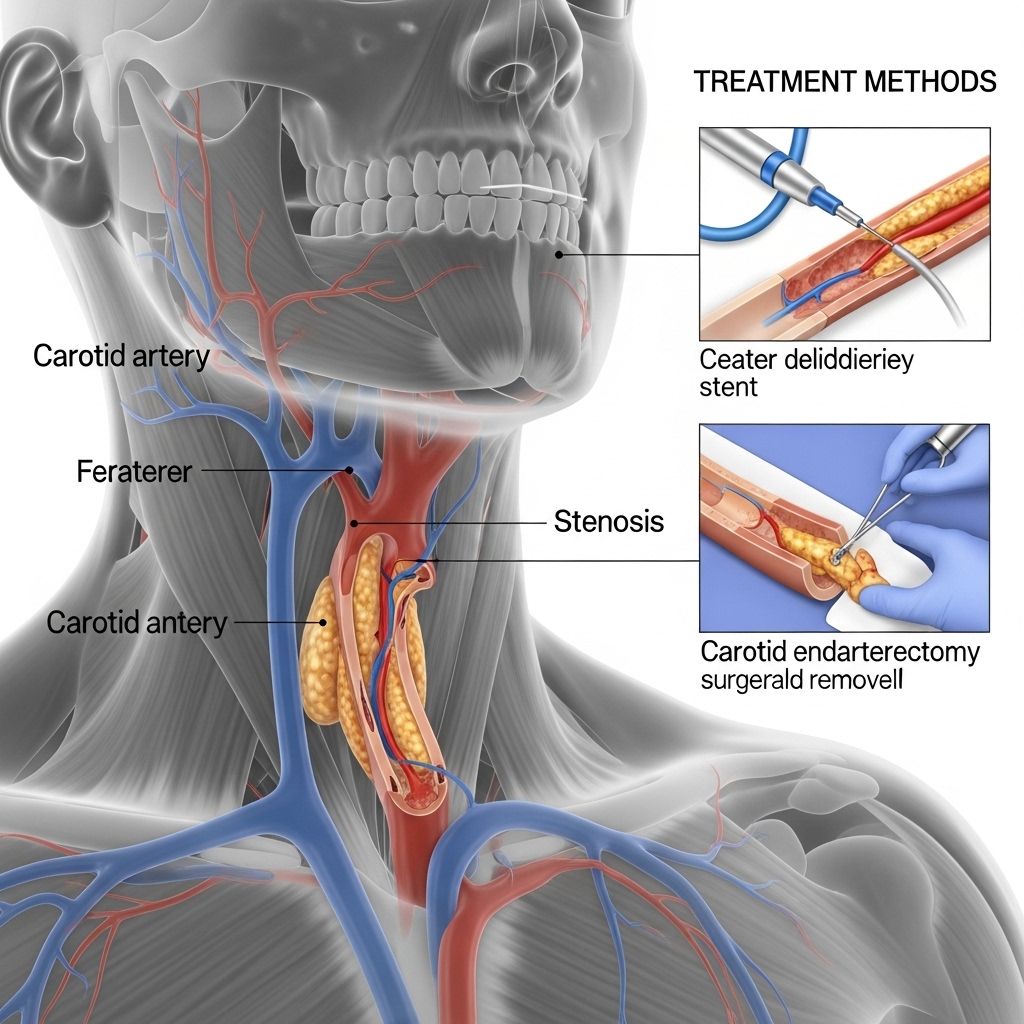
Your treatment plan will depend on the severity of your condition and your overall health. Our goal is to prevent a stroke and manage the disease effectively.
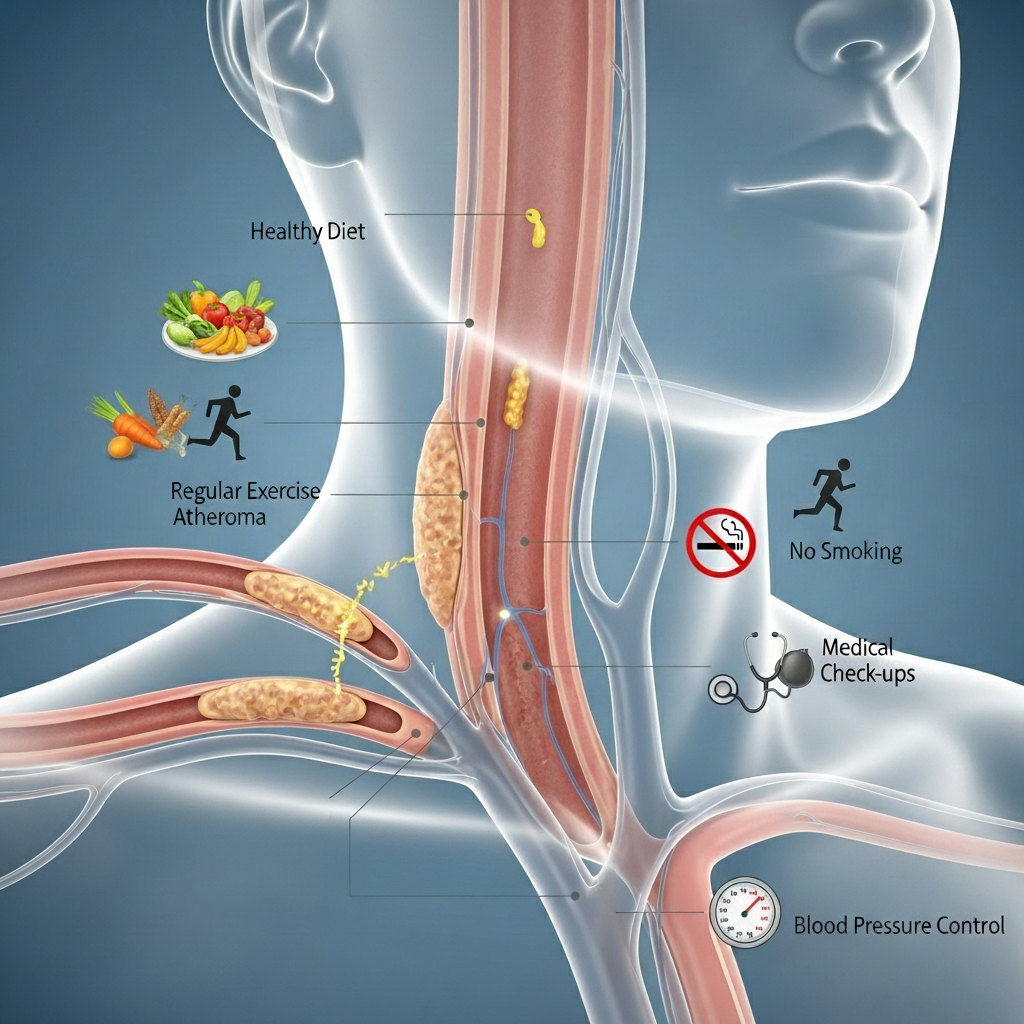
You can take proactive steps to lower your risk of developing carotid artery disease:
Any blockage in the carotid artery is a serious health concern because it significantly increases your risk of stroke. The severity depends on the degree of narrowing. Even moderate blockages warrant medical attention and management.
While you cannot completely reverse the plaque buildup, you can slow or stop its progression with lifestyle changes and medication. In some cases, treatment can help stabilize the plaque, making it less likely to cause a stroke.
Recovery varies depending on the treatment. For angioplasty and stenting, many patients can return to normal activities within a week. For a carotid endarterectomy, the recovery period may be slightly longer, typically a few weeks. Dr. Mughal will provide specific guidance based on your procedure.
Arteriovenous malformation of the colon can cause significant bleeding and anemia. While potentially serious, most cases respond well to appropriate treatment including endoscopic therapy or surgical intervention when necessary.