- 0317-4123373
- Bahria University Road D2 Johar Town Lahore, Pakistan
- Working Hour: Monday To Tuesday 04PM – 06PM
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a complex vascular condition that requires specialized medical expertise. Our comprehensive approach combines advanced diagnostics with personalized treatment plans to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
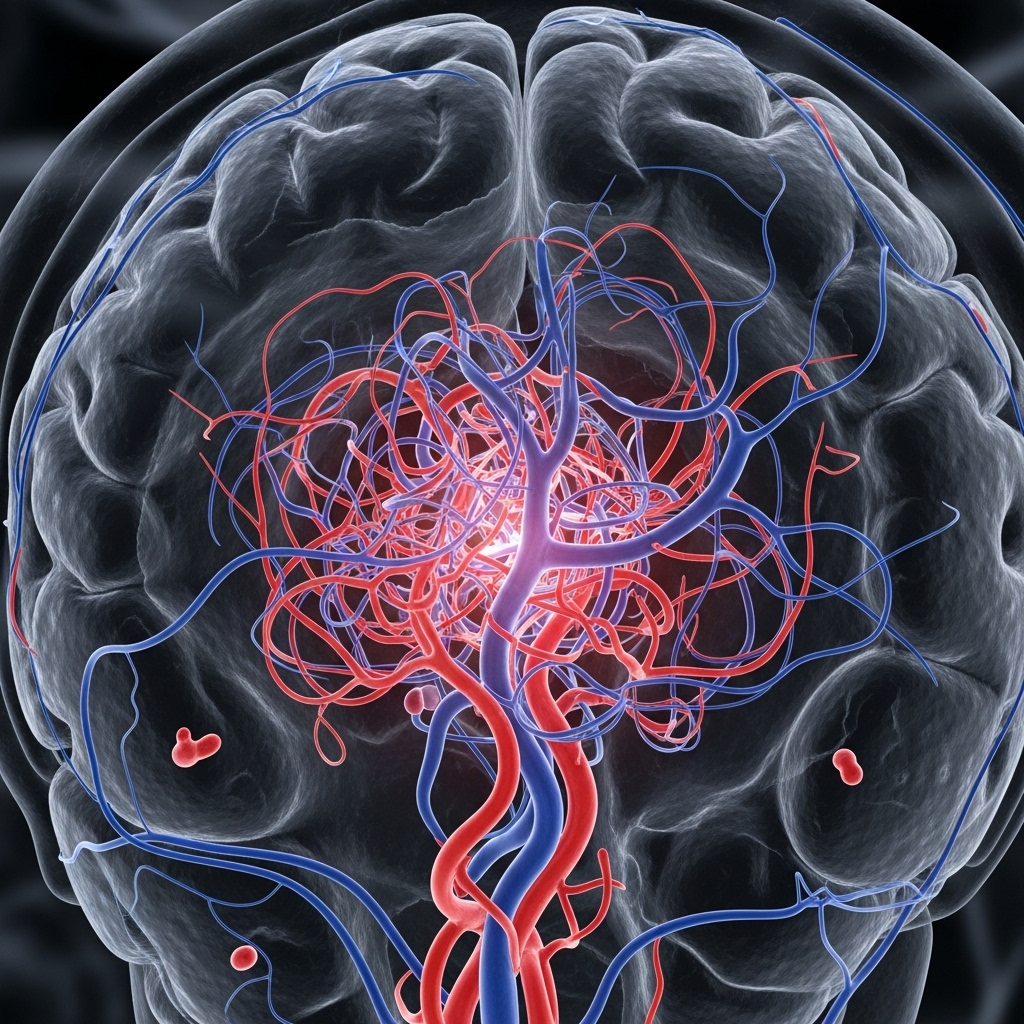
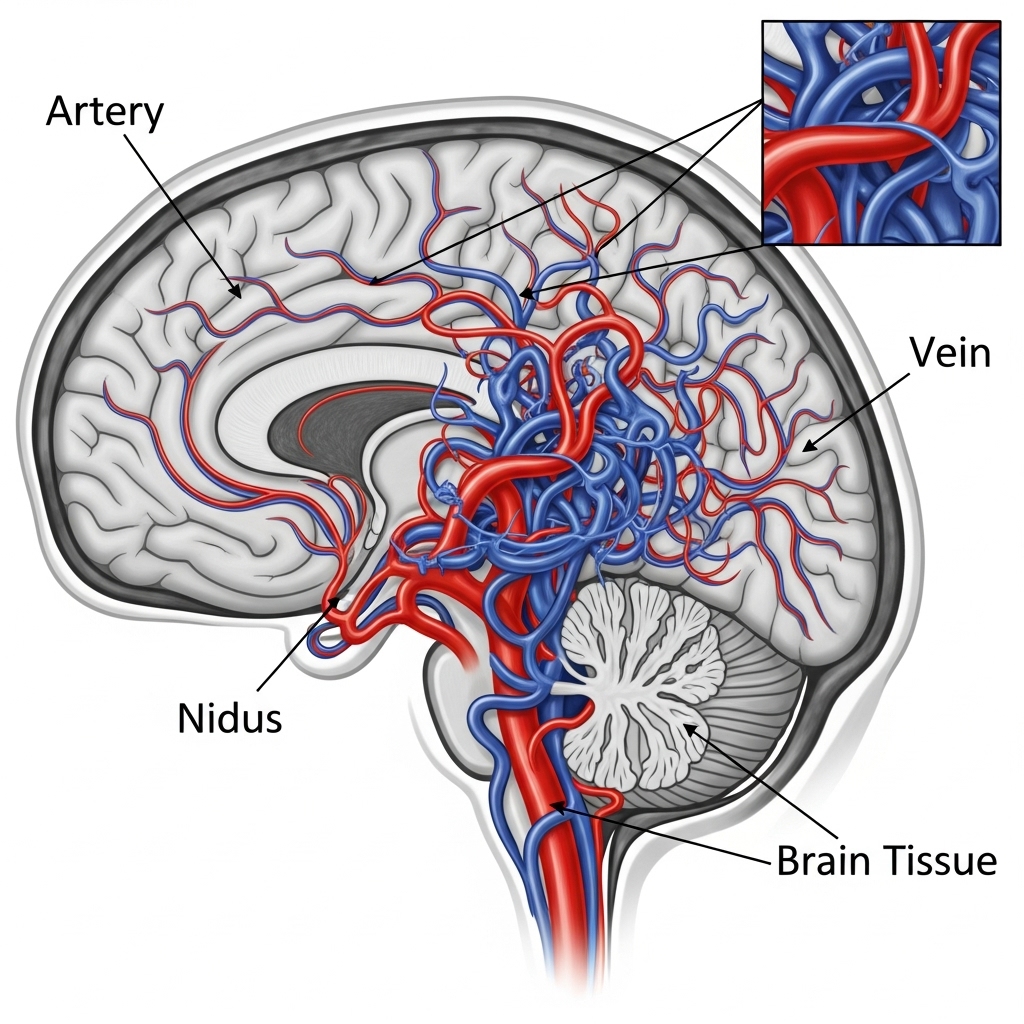
An arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins that bypasses the normal capillary system. These malformed blood vessels can occur anywhere in the body, including the brain, spinal cord, face, colon, and other organs. AVMs are typically congenital, meaning they develop before birth, though symptoms may not appear until later in life.
The abnormal vessel formation creates a direct pathway between high-pressure arteries and low-pressure veins, potentially leading to serious complications if left untreated.
Most arteriovenous malformations are congenital abnormalities that develop during fetal growth. The exact cause remains unclear, but researchers believe AVMs result from errors in vascular development during embryonic stages.
Arteriovenous malformation symptoms vary significantly depending on location, size, and blood flow patterns. Many patients remain asymptomatic for years, while others experience severe complications.
Peripheral AVMs
Gastrointestinal AVMs
Neurological AVMs:
Untreated arteriovenous malformations can lead to life-threatening complications requiring immediate medical intervention. Understanding these risks emphasizes the importance of early detection and treatment.
Hemorrhage:
Heart Failure:
Neurological Damage:
Local Tissue Damage:
Our comprehensive arteriovenous malformation radiology and treatment approach utilizes advanced diagnostic technologies and minimally invasive techniques for optimal patient outcomes.
Imaging Studies:
Specialized Testing:
Endovascular Procedures:
Surgical Interventions:
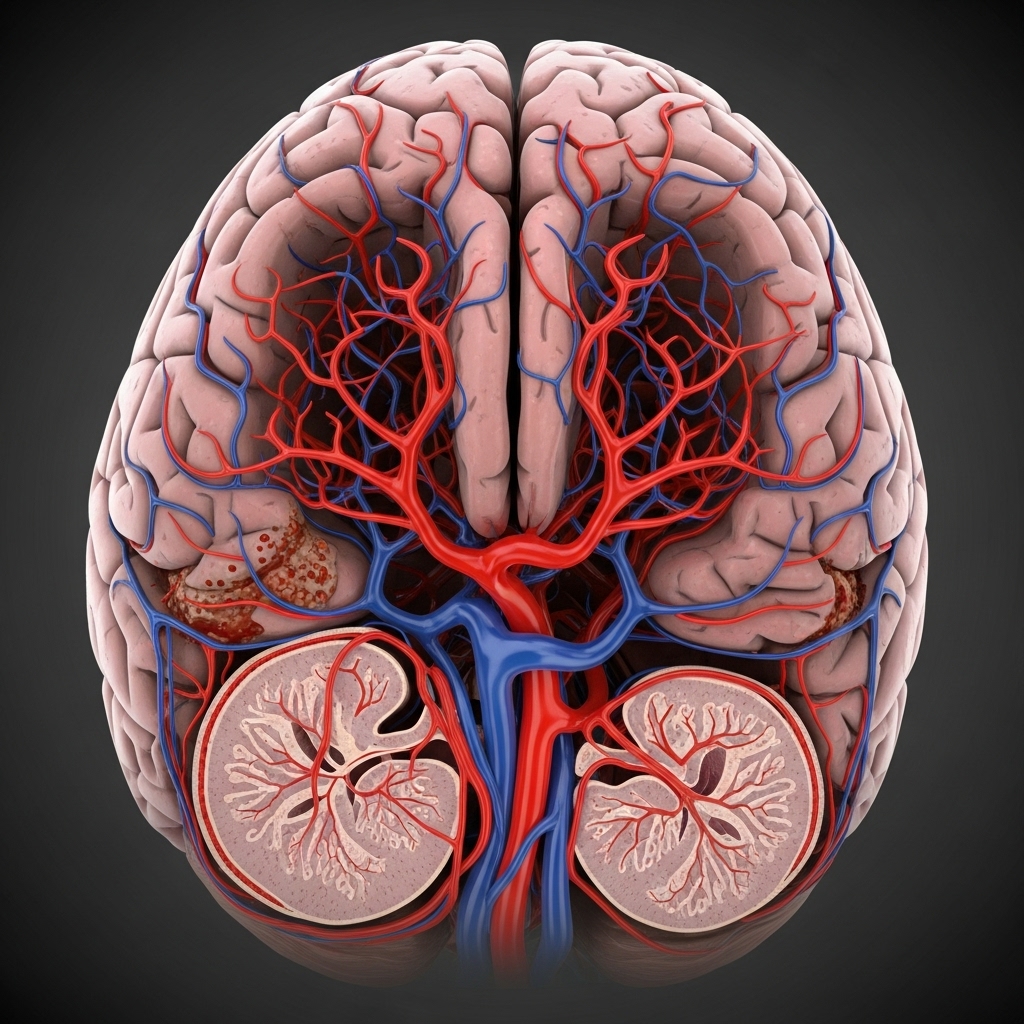
Post-treatment recovery requires comprehensive care and ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal healing and prevent complications.
Immediate Post-Treatment:
Short-term Recovery:
Long-term Management:
With appropriate treatment, most patients with arteriovenous malformation achieve excellent long-term outcomes and normal life expectancy.
Advanced diagnostics and minimally invasive treatment for arteriovenous malformation with our expert multidisciplinary team and state-of-the-art technology.
The ICD-10 codes for arteriovenous malformation vary by location. Common codes include Q28.2 for arteriovenous malformation of cerebral vessels and Q27.3 for peripheral vascular malformations. Your healthcare provider will use the appropriate code based on your specific diagnosis.
An arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels where arteries connect directly to veins without normal capillaries in between. This creates abnormal blood flow patterns that can cause various symptoms and complications.
While arteriovenous malformation pictures can provide educational information, proper diagnosis requires advanced imaging studies performed by qualified medical professionals. Clinical examination and specialized radiology are essential for accurate assessment.
Arteriovenous malformation of the colon can cause significant bleeding and anemia. While potentially serious, most cases respond well to appropriate treatment including endoscopic therapy or surgical intervention when necessary.
Yes, facial arteriovenous malformations can be effectively treated using various minimally invasive techniques including embolization and sclerotherapy. Treatment requires specialized expertise to preserve facial function and appearance.