9 Early Signs of Vascular Disease You Shouldn’t Ignore
Vascular disease refers to a range of conditions affecting your circulatory system, which includes the arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels. When these blood vessels have problems, it can lead to serious health issues. Early detection of vascular issues is critical for effective treatment and preventing complications. This guide will help you understand the early signs, why they are often overlooked, and when to seek professional medical advice.
Recognizing the subtle symptoms of poor circulation can be the first step toward protecting your long-term health. Many people dismiss early warning signs as normal parts of aging, but taking action promptly can make a significant difference in your outcomes.
What Is Vascular Disease?
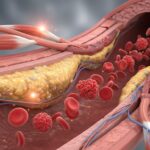
Any disorder that affects your blood vessels is considered vascular disease. This system is responsible for transporting blood, oxygen, and nutrients throughout your body. When blood flow is disrupted by blockages, narrowing, or weakening of the vessels, it can cause damage to organs and tissues.
Common types of vascular disease include:
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, most often the legs.
- Venous Disease: Conditions affecting the veins, such as varicose veins and deep vein thrombosis (DVT), often leading to blood flow problems in the legs.
- Carotid Artery Disease: Plaque buildup in the arteries of the neck that deliver blood to the brain, increasing stroke risk.
- Aneurysms: A bulge or weak spot in an artery wall, which can rupture and cause life-threatening bleeding.
Why Early Signs Are Often Ignored
Many hidden vascular symptoms are easily mistaken for less serious issues. For example, leg pain might be attributed to a tough workout, and fatigue is often blamed on a busy schedule. Because these symptoms can be subtle and develop gradually, people may not realize they are early PAD signs or indicators of other circulatory problems.
Ignoring these common vascular misconceptions can delay diagnosis and treatment, allowing the condition to progress. It is essential to listen to your body and understand that what seems like a minor inconvenience could be an early warning sign of a more significant health problem.
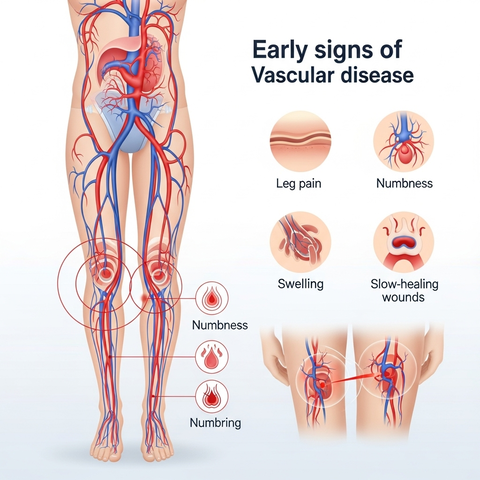
Early Signs of Vascular Disease
Here are nine early signs of vascular disease to watch for. If you experience any of these, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
1. Leg Pain or Cramping, Especially While Walking
One of the most common signs of PAD is claudication, which is muscle pain or cramping in the legs or arms that begins during exercise and ends with rest. This walking pain occurs because narrowed arteries cannot deliver enough oxygen-rich blood to meet the muscles’ demands during activity.
2. Numbness, Tingling, or Weakness in Limbs
Reduced blood flow can affect the nerves in your arms, legs, hands, and feet, causing unusual sensations. You might feel weak or if you have “pins and needles.” These symptoms of poor circulation are often overlooked but can indicate significant blood vessel blockage symptoms.
3. Cold Hands and Feet
If one limb feels colder than the other, it could be a sign of arterial narrowing. While having cold extremities is common, a noticeable temperature difference between limbs suggests that one is not receiving adequate blood flow, which may be a sign of peripheral circulation issues.
4. Slow-Healing Wounds or Ulcers
Poor blood supply impairs the body’s ability to heal. Wounds, sores, or ulcers on the feet, ankles, and legs that are slow to heal are a serious warning sign. These non-healing wounds, sometimes related to diabetic ulcers, require immediate medical attention to prevent infection and other complications.
5. Visible Vein Changes
Bulging, dark, or twisted veins, commonly known as varicose veins, can be more than a cosmetic issue. They often indicate underlying venous insufficiency, a condition where veins have trouble sending blood from the legs back to the heart. These visible vein problems can cause aching, swelling, and discomfort.
6. Skin Color Changes
A lack of adequate oxygen supply can cause noticeable changes in skin color. Your skin might appear pale, bluish (cyanosis), or have a shiny texture. This skin discoloration, especially blue legs from poor circulation, is a clear indicator that your vascular system is struggling.
7. Swelling in Legs or Ankles
Persistent swelling (edema) in your legs or ankles that worsens throughout the day can signal venous reflux or lymphatic issues. When veins are unable to circulate blood efficiently, fluid can accumulate in the lower limbs, causing discomfort and heaviness.
8. Weak Pulse in Legs or Feet
A weak or absent pulse in your legs or feet is a direct sign of reduced blood flow due to an artery narrowing. While often detected by a doctor during an examination, you may notice it yourself. It is a key indicator of potential circulation blockage.
9. Erectile Dysfunction in Men
For men, erectile dysfunction (ED) can be an early sign of vascular disease. The same arterial blockages that cause PAD can also restrict blood flow to the penis. Vascular ED is often one of the first clues that there are wider circulation issues.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
There are some things that make you more likely to get vascular disease:
- Smokers: Smoking is a primary risk factor for PAD and other vascular issues.
- Diabetics: Diabetes increases the risk of circulation problems and artery damage.
- High Blood Pressure or Cholesterol: These conditions contribute to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Family History: If you have a hereditary tendency, your risk may go up.
- Age: Individuals over 45 are more susceptible.
When to See a Doctor
You should schedule a checkup with a vascular specialist if you experience:
- Persistent pain in your legs, especially when walking.
- Wounds on your feet or legs that will not heal.
- Unusual swelling, discoloration, or temperature changes in your limbs.
- Discomfort from visible, bulging veins.
For expert diagnosis and care, finding the best vascular doctor is crucial. For those seeking a specialist, Vascular Care is a leading service provider dedicated to advanced, patient-focused treatments.
How Vascular Disease Is Diagnosed
To diagnose vascular conditions, a doctor may use several tests:
- Doppler Ultrasound: This non-invasive scan uses sound waves to visualize blood flow and identify blockages.
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): A simple test that compares blood pressure in your ankle with the pressure in your arm to screen for PAD.
- CT Angiography: An imaging test that uses X-rays and a special dye to create detailed pictures of your blood vessels.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment options range from lifestyle adjustments to advanced procedures:
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, exercising, and managing weight are fundamental vascular health tips.
- Medications: Drugs to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, and prevent blood clots are often prescribed.
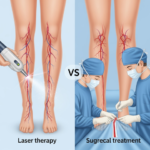
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques like angioplasty, stenting, and laser treatments can open blocked arteries and treat varicose veins with less risk and faster recovery.
Prevention is key. A heart-healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure can significantly lower your risk of developing vascular disease.
Take Control of Your Vascular Health
Recognizing the early signs of vascular disease is the first step toward preventing serious complications. If you have symptoms of poor circulation in your legs or any other concerns, do not hesitate to seek a medical evaluation. A timely diagnosis can lead to effective treatments that improve your quality of life and protect your health for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the common symptoms of vascular disease?
The most common symptoms include pain or cramping in the legs during activity (known as claudication), numbness or weakness in the extremities, cold or pale legs and feet, and slow-healing sores. If you notice these signs, it is important to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Who is at risk for vascular disease?
Individuals with a family history of vascular conditions, those who smoke, people with diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol levels, and individuals over 50 years old are at a higher risk of developing vascular disease. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk.
How is vascular disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves a combination of a physical examination, reviewing your medical history, and specialized tests such as ultrasounds, blood flow measurements, or angiography. Your doctor will recommend the best approach based on your symptoms and health profile.
Can vascular disease be treated?
Yes, vascular disease is treatable through a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Early diagnosis greatly improves the success of treatment, making it essential to address symptoms as soon as they appear.
How can I prevent vascular disease?
Preventative measures include maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, quitting smoking, and attending regular check-ups. Building healthy habits can drastically reduce your risk of vascular complications.
If you have additional questions about your vascular health, always consult your healthcare provider for reliable, personalized guidance.