Vascular Meaning in Urdu: Complete Blood Vessel Health Guide
Understanding vascular health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being, especially as cardiovascular diseases remain leading causes of mortality worldwide. The term “vascular” encompasses everything related to our blood vessels, and knowing its meaning in both English and Urdu can help bridge language barriers in healthcare communication.
What is Vascular Disease?
Vascular disease refers to any condition that affects the circulatory system, specifically the network of blood vessels that carry blood throughout the body. These conditions can range from minor circulation problems to life-threatening emergencies requiring immediate medical attention.
The vascular system serves as the body’s highway system, delivering oxygen and nutrients to every cell while removing waste products. When this system becomes compromised, it can lead to serious health complications affecting multiple organs and body systems.
Vascular Meaning in Urdu and English
Understanding medical terminology in both languages helps improve healthcare communication:
Vascular meaning in Urdu: خون کی نالیوں سے متعلق (Khoon ki naliyon se mutaliq)
- This translates to “related to blood vessels”
Vascularized meaning in Urdu: خون کی رسائی والا (Khoon ki rasai wala)
- This means “supplied with blood vessels”
Vascularity meaning in Urdu: خون کی نالیوں کی فراہمی (Khoon ki naliyon ki farahmi)
- This refers to “the supply of blood vessels”
The word “vascular” comes from the Latin word “vasculum,” which meaning “little vessel.” It describes anything related to or consisting of vessels that carry fluids, particularly blood and lymph.
Types of Blood Vessels Involved
There are three primary types of blood vessels in the vascular system, and each one does a particular job:
Arteries
Arteries carry blood with a lot of oxygen from the heart to other sections of the body. These vessels have thick, muscular walls that can withstand high pressure from the heart’s pumping action. The aorta, the body’s largest artery, branches into smaller arteries that distribute blood throughout the body.
Veins
Veins transport oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Unlike arteries, veins have thinner walls and contain one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. Vena cavae are the biggest veins that take blood back to the heart.
Capillaries
Capillaries are the tiniest blood vessels. They join arteries and veins. These microscopic vessels allow for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between blood and tissues. Their thin walls enable efficient transfer of substances.
General Impact on Health
Vascular health significantly affects overall wellness. Healthy blood vessels ensure proper circulation, maintaining optimal blood pressure and delivering essential nutrients to organs. Poor vascular health can lead to reduced quality of life, limited mobility, and increased risk of serious complications.
The cardiovascular system works continuously, with the heart pumping approximately 5 liters of blood per minute through thousands of miles of blood vessels. Any disruption in this system can have far-reaching consequences for physical and mental health.
Types of Vascular Disease
Several conditions can affect the vascular system:
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
PAD occurs when arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the extremities. This condition commonly affects the legs and can cause pain, numbness, and difficulty walking.
Coronary Artery Disease
The coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrower or obstructed as a result of this condition. It can cause chest pain, heart attacks, and other serious heart problems.
Cerebrovascular Disease
This category includes conditions affecting blood vessels in the brain, such as stroke and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). These conditions can cause permanent neurological damage if not treated promptly.
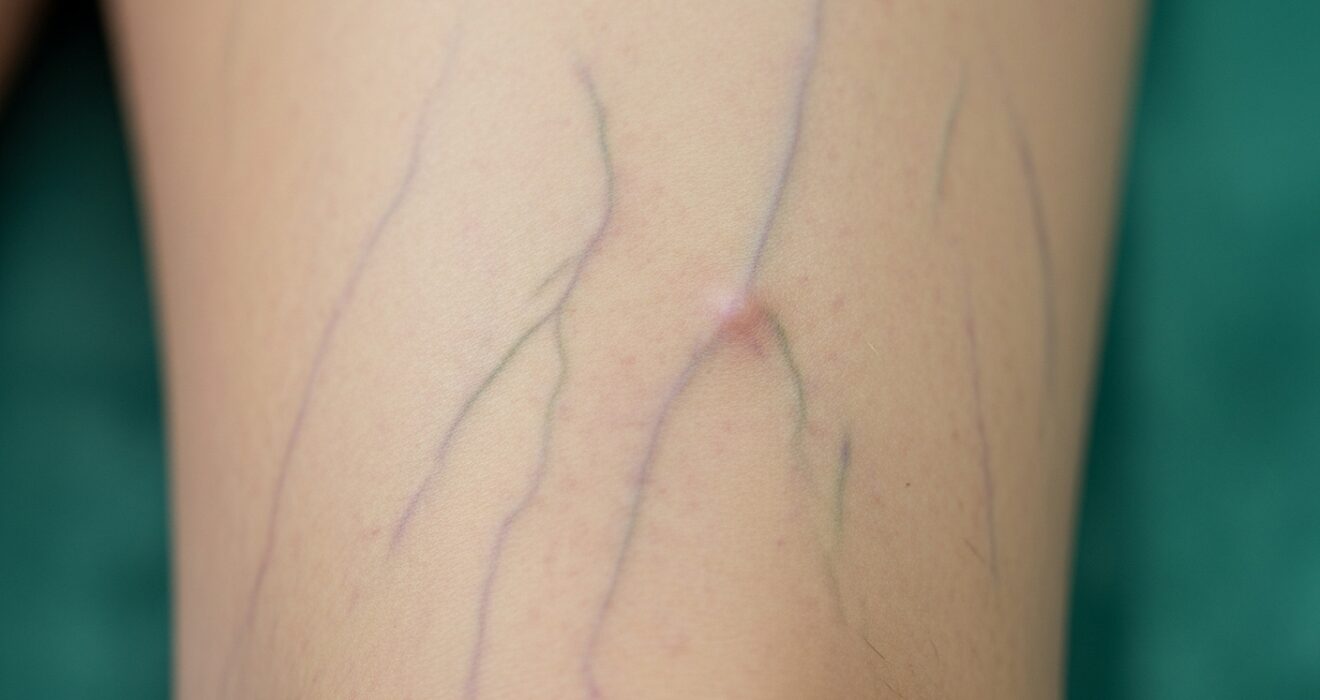
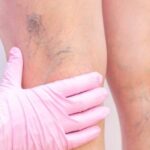
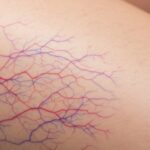
Venous Disorders
Some problems that can happen with veins are varicose veins, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and chronic venous insufficiency. These conditions affect the return of blood to the heart and can cause pain, swelling, and skin changes.
Aortic Aneurysms
Aneurysms are weak areas in the wall of blood vessels. Aortic aneurysms can be life-threatening if they rupture, requiring immediate medical intervention.
Symptoms
Vascular disease symptoms vary depending on the affected vessels and severity of the condition:
Common symptoms include:
- Leg pain or cramping during physical activity
- Numbness or weakness in extremities
- Cold hands or feet
- Slow-healing wounds
- Changes in skin color or texture
- Swelling in legs or feet
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Sudden severe headaches
- Vision changes or speech difficulties
Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing serious complications.
Causes
Multiple factors contribute to vascular disease development:
Primary causes include:
- Atherosclerosis (buildup of plaque in arteries)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Diabetes mellitus
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Genetic predisposition
- Age-related changes in blood vessels
- Inflammatory conditions
- Blood clotting disorders
Understanding these causes helps identify individuals at higher risk and implement appropriate preventive measures.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing vascular disease:
Modifiable risk factors:
- Smoking
- Poor diet high in saturated fats
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Non-modifiable risk factors:
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Gender (men generally at higher risk)
- Family history of vascular disease
- Certain genetic conditions
- Ethnicity (some groups have higher predisposition)
Complications
Untreated vascular disease can lead to serious complications:
- Heart attack or cardiac arrest
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack
- Kidney disease or failure
- Limb amputation
- Gangrene
- Pulmonary embolism
- Chronic pain and disability
- Reduced quality of life
These complications underscore the importance of early detection and appropriate treatment of vascular conditions.
Prevention
Preventing vascular disease involves lifestyle modifications and regular medical care:
Lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Exercise regularly (at least 150 minutes per week)
- Quit smoking and avoid tobacco products
- Maintain healthy weight
- Manage stress effectively
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Stay hydrated
Medical management:
- Regular blood pressure monitoring
- Cholesterol level checks
- Diabetes management
- Medication compliance
- Regular medical check-ups
Diagnosis and Tests
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose vascular disease:
Diagnostic tests include:
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI)
- Duplex ultrasound
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA)
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- Conventional angiography
- Blood tests for cholesterol and diabetes
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
By assessing the degree and severity of vascular disease, these tests aid in the decision-making process for treatment.
Treatment Options
The exact ailment and its severity determine the different treatment approaches:
Non-surgical treatments:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Medications (blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs)
- Supervised exercise programs
- Smoking cessation programs
- Dietary counseling
Surgical interventions:
- Angioplasty and stent placement
- Bypass surgery
- Endarterectomy
- Minimally invasive procedures
- Laser treatments for varicose veins
Management and Treatment
Effective vascular disease management requires a comprehensive approach:
Key components include:
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care
- Medication adherence
- Lifestyle modification support
- Patient education
- Multidisciplinary team approach
- Emergency action plans
- Family involvement in care
Long-term success depends on patient commitment to treatment plans and lifestyle changes.
Related Health Topics
Vascular health connects to various other health conditions:
- Diabetes management
- Hypertension control
- Cardiac rehabilitation
- Wound care and healing
- Nutrition and dietary planning
- Exercise physiology
- Smoking cessation
- Stress management
Frequently Asked Questions
What does vascular mean in simple terms?
Vascular refers to anything related to blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries that carry blood throughout the body.
How do I know if I have vascular problems?
Common signs include leg pain during walking, slow-healing wounds, cold extremities, and changes in skin color. Consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
Can vascular disease be prevented?
Many forms of vascular disease can be prevented through healthy lifestyle choices, including regular exercise, healthy diet, not smoking, and managing chronic conditions.
Is vascular disease hereditary?
While genetics play a role, lifestyle factors significantly influence vascular health. Having a family history increases risk but doesn’t guarantee developing the condition.
When should I see a vascular specialist?
Consult a vascular specialist if you experience persistent leg pain, slow-healing wounds, or have multiple risk factors for vascular disease.
Taking Control of Your Vascular Health
Understanding vascular meaning in Urdu and English helps bridge communication gaps in healthcare settings. Vascular health forms the foundation of overall well-being, affecting every organ system in the body. By recognizing symptoms early, understanding risk factors, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing serious vascular conditions.
Remember that vascular disease is often preventable and manageable with proper care. Regular medical check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and adherence to treatment plans can help maintain optimal vascular health throughout life. Do not be reluctant to seek competent medical examination and treatment if you suspect vascular issues.